Technical Issues Related to the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (2002)
Chapter: Color Plates
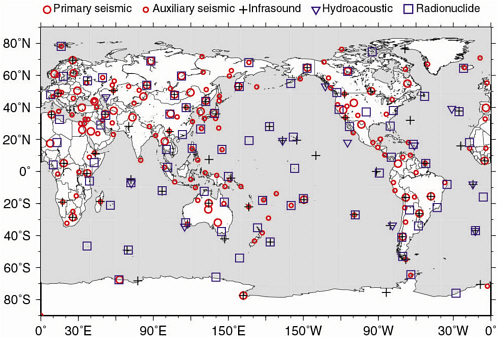
Figure 2–1 A global map showing five networks of IMS stations, which use the technologies of seismology, infrasound, hydroacoustics, and radionuclides. Data from all these stations are telemetered to the IDC in Vienna. Certified laboratories at 16 locations, not shown, contribute to the analysis of radionuclide data. (Figure courtesy of W.Y.Kim.)
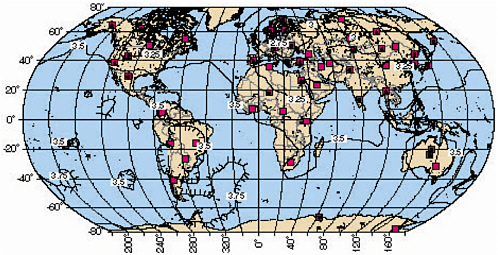
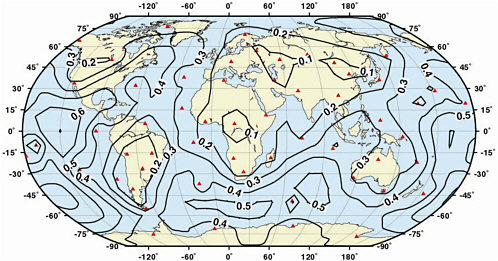
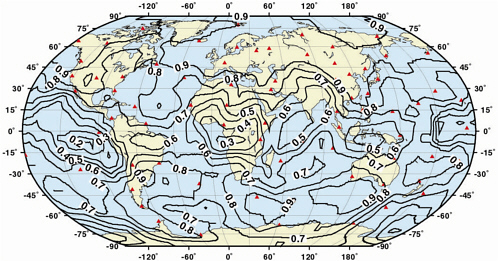
Figure 2–2 Contours of seismic magnitude for which signals would be expected (with signal-to-noise amplitude ratio greater than 3.2, i.e. 10 dB) at three or more stations of the IMS primary seismic network (solid squares), from 90 percent of the events at the contoured magnitude or larger. The contour interval is 0.25 magnitude units. The detection threshold for Europe, Asia, North America, and North Africa is in the magnitude range 3.5 to 3 or lower. (Figure provided by the Center for Monitoring Research)
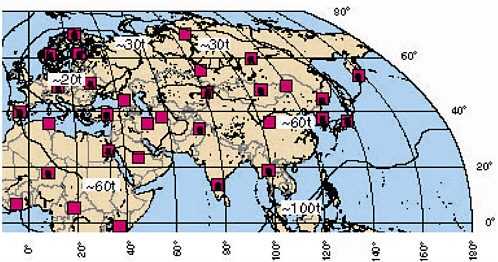
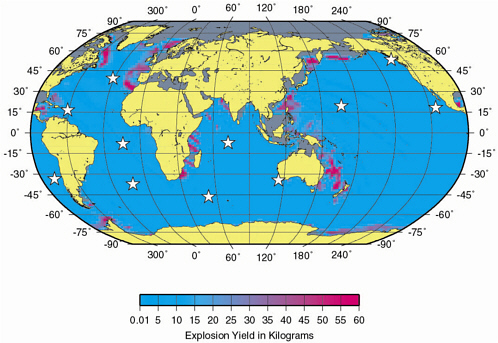
Figure 2–3 Contours of approximate yield for tamped explosions, for which detections can be expected at three IMS primary stations (solid squares). These contours are the same as those of Figure 2–2, but with an expanded view of Europe, Asia and North Africa, and using the approximate yields of Table 2–2 (expressed now in tons rather than kilotons) to interpret seismic magnitudes.
There was a problem loading page 91.