Finding Hazardous Asteroids Using Infrared and Visible Wavelength Telescopes (2019)
Chapter: 7 Impact Hazards Not Explicitly Considered by the George E. Brown, Jr. Act
7
Impact Hazards Not Explicitly Considered by the George E. Brown, Jr. Act
Near Earth objects (NEOs) are not the only objects in space that can potentially impact Earth. As understanding of the solar system has advanced and more telescopic observations have been made, scientists have identified other objects that could pose an impact hazard and are also of scientific interest. These are summarized in this chapter for the sake of completeness.
JUPITER-FAMILY AND LONG-PERIOD COMETS
It is possible for comets from the outer solar system to cross Earth’s orbit.
- Short-period comets (also referred to as Jupiter-family comets, JFCs) with orbital periods of typically less than 20 years;
- Long-period comets (LPCs), including isotropic comets and Halley-type comets (HTCs), with longer orbital periods.
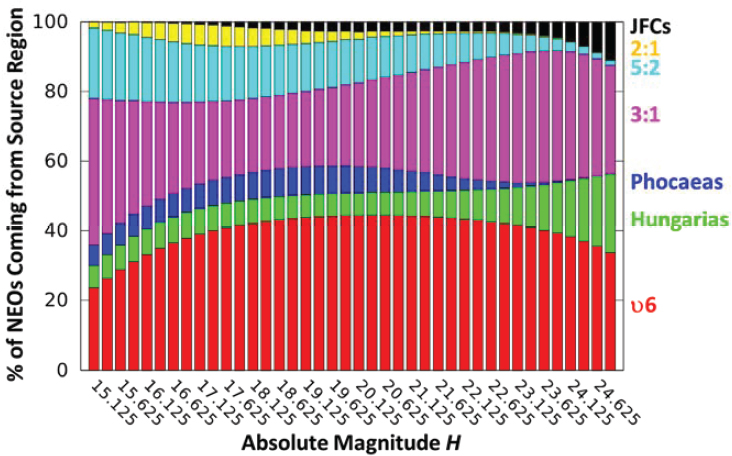
The contribution of multiple NEO source regions is shown in Figure 7.1. Most NEOs come from the inner and central main belts; few come from the outer main belt or JFCs. For LPC and HTC populations, the goal should be to know the number-flux density of such comets (i.e., the number of comets per unit time per size bin) through near-Earth space, because the absolute number is huge and it is extremely difficult to identify them all individually, because the vast majority are too distant.
OBJECTS WITH DIAMETERS LESS THAN 140 METERS
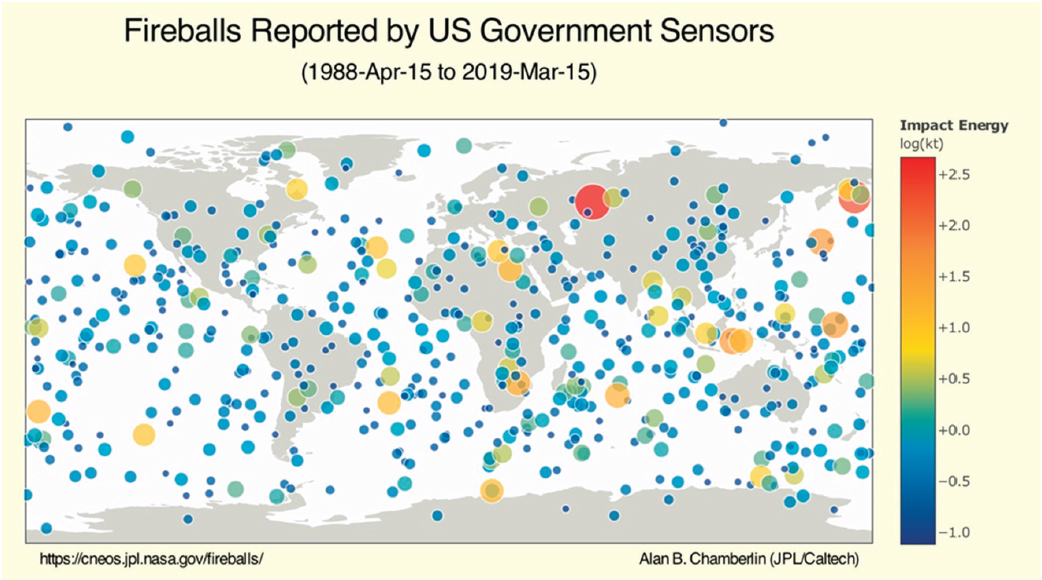
The George E. Brown, Jr. Near-Earth Object Survey Act specified 140 meters as the lower limit for the NEO survey requirements in the 2005 NASA Authorization Act. Objects smaller than 140 meters are being found and catalogued in existing visible surveys. Although the completeness level of these surveys is low, it is important to discover and catalogue these objects. The 2013 Chelyabinsk fireball and the December 2018 fireball that exploded over the western Pacific Ocean had energies of 440 and nearly 200 kilotons, respectively. The Chelyabinsky fireball resulted in major damage to buildings. Both meteoroids were estimated to be significantly smaller than 140 meters in diameter (see Figure 7.2).
INTERSTELLAR OBJECTS
Interstellar objects, of which only one has been discovered in the history of astronomy, can be treated as part of the LPC population and are a miniscule fraction thereof.
- The probability of an impact by an LPC is only 1 percent that of a NEO impact.1
- The energy of an Earth impact would be high, because velocity at Earth orbit would be high, and energy is proportional to square of velocity and is calculated at ~30 percent larger than a typical NEO impact.
Definitions of these types of NEOs are included in this report for the sake of completeness and to explain why they should be considered within the context of the George E. Brown Act requirement, although they are not a driver in meeting the requirement.
___________________
1 G.H. Stokes, B.W. Barbee, W.F. Bottke, Jr., M.W. Buie, S.R. Chesley, P.W. Chodas, J.B. Evans, et al., 2017, Report of the Near-Earth Object Science Definition Team: Update to Determine the Feasibility of Enhancing the Search and Characterization of NEOs, NASA Science Mission Directorate, https://cneos.jpl.nasa.gov/doc/2017_neo_sdt_final_e-version.pdf.


