Sustaining Zero-Fare Public Transit in a Post COVID-19 World: A Guide for State DOTs (2024)
Chapter: 1 Introduction

CHAPTER 1
Introduction
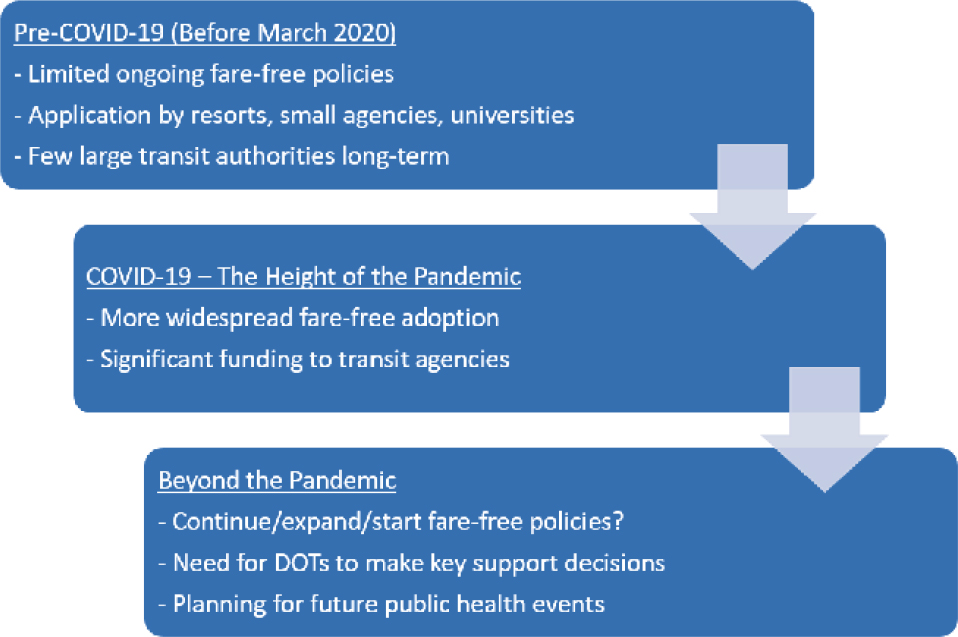
Fare-free transit service is not a new concept in the United States. Fare-free policies were in place or had been tested in many locations throughout the United States prior to the COVID-19 pandemic. These locations predominantly included large rural areas serviced by smaller transit systems, resort areas with high visitor volumes, and university-dominated communities. The decreased fare revenues were offset by greatly increased ridership levels, decreased fare collection expenses, and increased levels of service to those riders most sensitive to fares. However, these fare-free policies sometimes resulted in overloaded vehicles and an increased presence of disruptive passengers.
The COVID-19 pandemic proved difficult for transit agencies seeking to serve the needs of the public while sustaining a safe environment for employees and passengers. Building and maintaining ridership are never easy, and the impacts of the pandemic, which began in March 2020, were dramatic on ridership. In addition to health safety measures and service changes, many transit agencies suspended fares. This fare suspension helped eliminate cost/process barriers for riders needing the service the most and provided for contactless boarding procedures.
As many transit authorities consider continuing or moving to fare-free policies, state departments of transportation (DOTs) will be challenged to assist transit agencies in their states with implementation. Understanding the benefits and risks of this policy decision will allow transit agencies to have the best opportunity to succeed in serving all riders, but especially the most disadvantaged and underserved. Figure 1 shows the progression of fare-free policies in the United States.
Fare-free transit is top of mind with many agencies and the public. It was even the topic of a recent Freakonomics podcast (Dubner, 2022).
Building on the insights obtained from earlier research, this project provides guidance for evaluating the implementation of fare-free transit service policies by state DOTs and transit agencies. The guide and accompanying practitioners’ tool developed as part of this study provide users with the means to make informed decisions and recommendations without advocating for or against the implementation of fare-free service. The tool can be found on the National Academies Press website (nap.nationalacademies.org) by searching for NCHRP Research Report 1126: Sustaining Zero-Fare Public Transit in a Post COVID-19 World: A Guide for State DOTs.
1.1 Problem Statement
The objective of this guide and the tool is to provide a clear, user-friendly means for state DOTs (and transit agencies) to evaluate, support, and oversee the initiation, continuation, or discontinuation of fare-free transit services. With a focus on long-term sustainability, the research team developed a practitioner-ready tool for evaluating the benefits and risks of fare-free transit services and provided the necessary background guidance to effectively support such
an evaluation at all levels of government and among different stakeholders. The study results frame the development of a process and products intended to assist state DOTs throughout their consideration of fare-free transit service continuation or implementation.
1.2 Research Approach
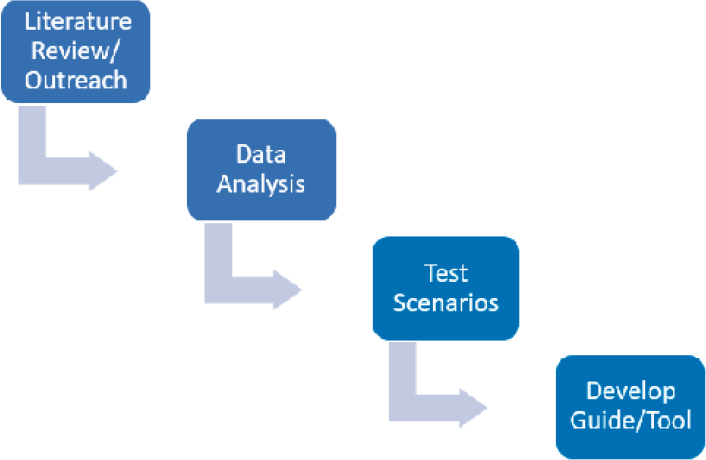
The development of this guide and practitioners’ tool was based on a thorough investigation of the current state-of-practice and operational experiences. A literature review [inclusive of domestic and international sources, the National Transit Database (NTD), and partial fare-free operations] was coupled with outreach to select agencies to learn about the benefits realized and the challenges faced directly by the service providers. This information was then incorporated into a comprehensive guidance document and used to develop a spreadsheet tool that was subsequently tested against a range of likely scenarios. A guiding principle of this research was not to advocate for or against fare-free transit services in any form or produce a process that yields a definitive answer. Instead, the goal of this research was to provide the necessary support for informed decision-making in a state DOT’s (or transit agency’s) unique context. Figure 2 shows the research approach for this study.
1.3 Tool Development
The practitioners’ tool was developed using a common spreadsheet platform (Microsoft Excel) to provide the broadest opportunity for use and longevity. Usage instructions are embedded in the spreadsheet with clear data entry prompts (e.g., drop-down menus, recommended ranges) that allow users to quickly build scenarios and generate outputs containing both quantitative and qualitative elements. A summary report is provided as a separate worksheet, and multiple scenarios can be run and compared. While input data ranges based on previous research are built into the spreadsheet, the tool is not restrictive in the assumptions that can be evaluated.
1.4 Target Audience/Users
The target audience for the guide and tool is state DOTs (and transit agencies) that are considering starting, continuing, or stopping fare-free transit services (full or partial). The specific target user is a staff member at a state DOT or transit agency who has been tasked with completing an evaluation of potential options for starting, continuing, or stopping fare-free transit services; providing a clear, unbiased understanding of the potential benefits/challenges of each option; and performing these tasks with the confidence of the assembled industry knowledge and experience presented in this guide.


